What is Planned Maintenance Percentage, or PMP? As the name suggests, planned maintenance percentage is a percentage that describes the amount of maintenance time used towards planned maintenance tasks, which is measured against the total amount of maintenance hours in a given time period (weeks, months, years). It provides a side-by-side comparison of the volume of scheduled maintenance and unplanned maintenance tasks you are performing.
Monitoring your PMP metric is a straightforward yet effective way to measure the performance of your maintenance efforts and processes. For instance, if your PMP is low (i.e. a minimal amount of maintenance hours is spent on planned maintenance), there could be an issue with production equipment that’s keeping it from functioning at an appropriate level. On the other hand, a high PMP means that your maintenance program is efficient. The majority of tasks are planned and breakdowns are limited, which means downtime is low.
How do you calculate PMP?

Industry goals for PMP are around 80%, and numbers that exceed that are considered world-class.
For example, say the maintenance team of a metalworking factory performs 500 hours of maintenance in a month. Of those 500 hours, 400 of them are planned maintenance hours. This makes our equation:
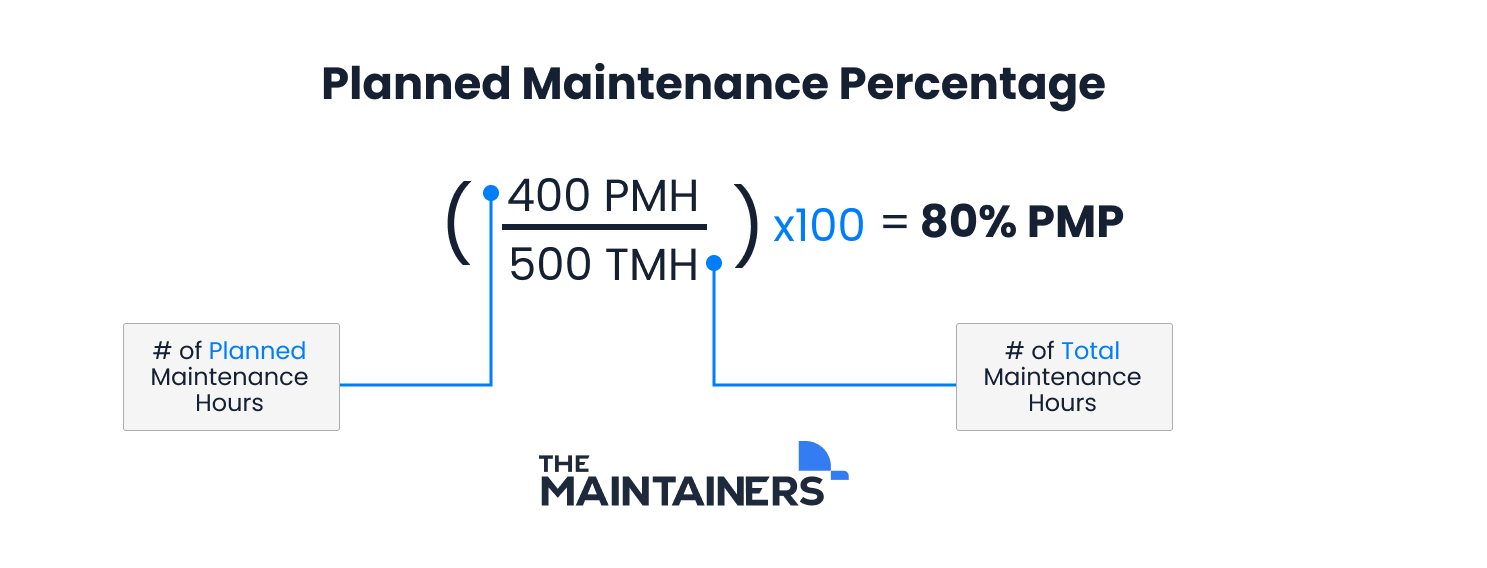
To accurately calculate your PMP, hours must be rigorously documented. Maintenance software like an enterprise asset management (EAM) system, or a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS) are useful tools to keep track of this information.
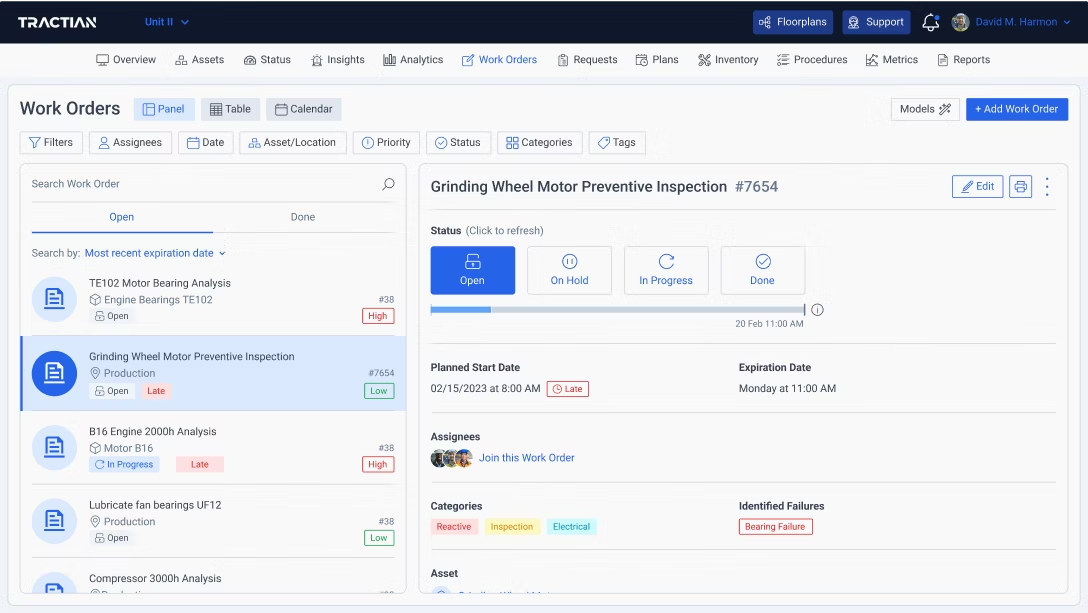
TRACTIAN’s TracOS monitors and analyzes the hours logged in work orders, allowing managers to assess the efficiency of task completion, as well as what exactly has been done and by whom. This way, managers can easily pull reports on planned and unplanned maintenance hours and apply the formula above.
It’s important to remember that your planned maintenance percentage is reflective of your baseline. While the industry goal is 80%, the reality is that most maintenance teams have much lower numbers, with the lowest being directly related to organizations that predominantly rely on reactive maintenance practices.
How to Improve your PMP?
As we mentioned earlier, a low PMP means a majority of your maintenance time is spent on unplanned maintenance. This typically indicates that an asset is having deeper problems—it fails and needs to be correctively maintained instead of being maintained when planned.
The most effective method to increasing PMP is by creating a detailed schedule, and ensuring teams stick to it. This means having good schedule compliance, a number that tracks how many scheduled maintenance tasks have been completed on time compared to the number scheduled. Low schedule compliance means you are missing tasks or deprioritizing them due to unexpected failures or other maintenance distractions, i.e. you might be in fire-fighting mode. Fire-fighting happens when you aren’t working on tasks needed to improve equipment reliability because the reliability is so poor – creating a vicious circle of ever-decreasing reliability.
That being said, there are more factors involved in improving schedule compliance than simply saying “stick to the schedule.” Here are some considerations and methods to improve your schedule compliance and in turn, your PMP:
- Consider skill level.
An experienced technician will be able to complete tasks faster than a new, inexperienced one. Matching the maintenance activities with the skills of your team increases their effectiveness. With proper planning, you can optimize your maintenance by leveraging the right people for the right tasks.
- Analyze your assets, and plan for them.
Gather thorough information on your assets. How often is maintenance required on it? How often do they fail? What caused the failure? By examining its failure modes, you can formulate a strategy to mitigate and/or correct the issue, should it arise. If an asset needs more work, adapt your maintenance plan accordingly.
With TRACTIAN’s TracOS™, asset management and analysis is fully digitized and streamlined. Once you input an asset’s information onto the platform, you can pull up its complete history, from previous work orders and performed maintenance tasks to costs and inventory. The app also generates key performance indicators that highlight the asset’s health and performance and can schedule maintenance tasks for you, building a healthy preventive maintenance strategy that suits your needs best.
- Improve documentation.
Establish good process workflows and ensure your technicians are able to access them. Rigorously track asset maintenance history, so your maintenance teams can quickly identify recurring issues and remedies. Properly documenting all necessary procedures, especially in emergencies and critically important cases allows for faster decision making, and less unplanned maintenance hours.
- Implement an EAM.
Enterprise asset management (EAM) software is a game changer for setting schedules, creating, monitoring, and facilitating efficient completion of work orders with set instructions and machine history. Having this information available to all members of the team means everyone is on the same page, and allows managers to quickly see where maintenance hours are going.
- Listen to your team.
Regularly speak with your technicians and other people on the team to gather feedback and see what is missing from your schedule. Whether it be additional training for less experienced team members, or needing to redistribute tasks, knowing where your team stands and how they feel will help you more effectively plan for the future.
- Invest in your effort.
In order to reach optimal levels of both costs and performance, additional spending above regular labor and material will be needed. This can come in the form of hiring more technicians or specialists, increasing man hours to tackle preventive tasks, or investing in a top-tier EAM software. Increasing your funding to develop best practices helps you get closer to that goal of 80% PMP.
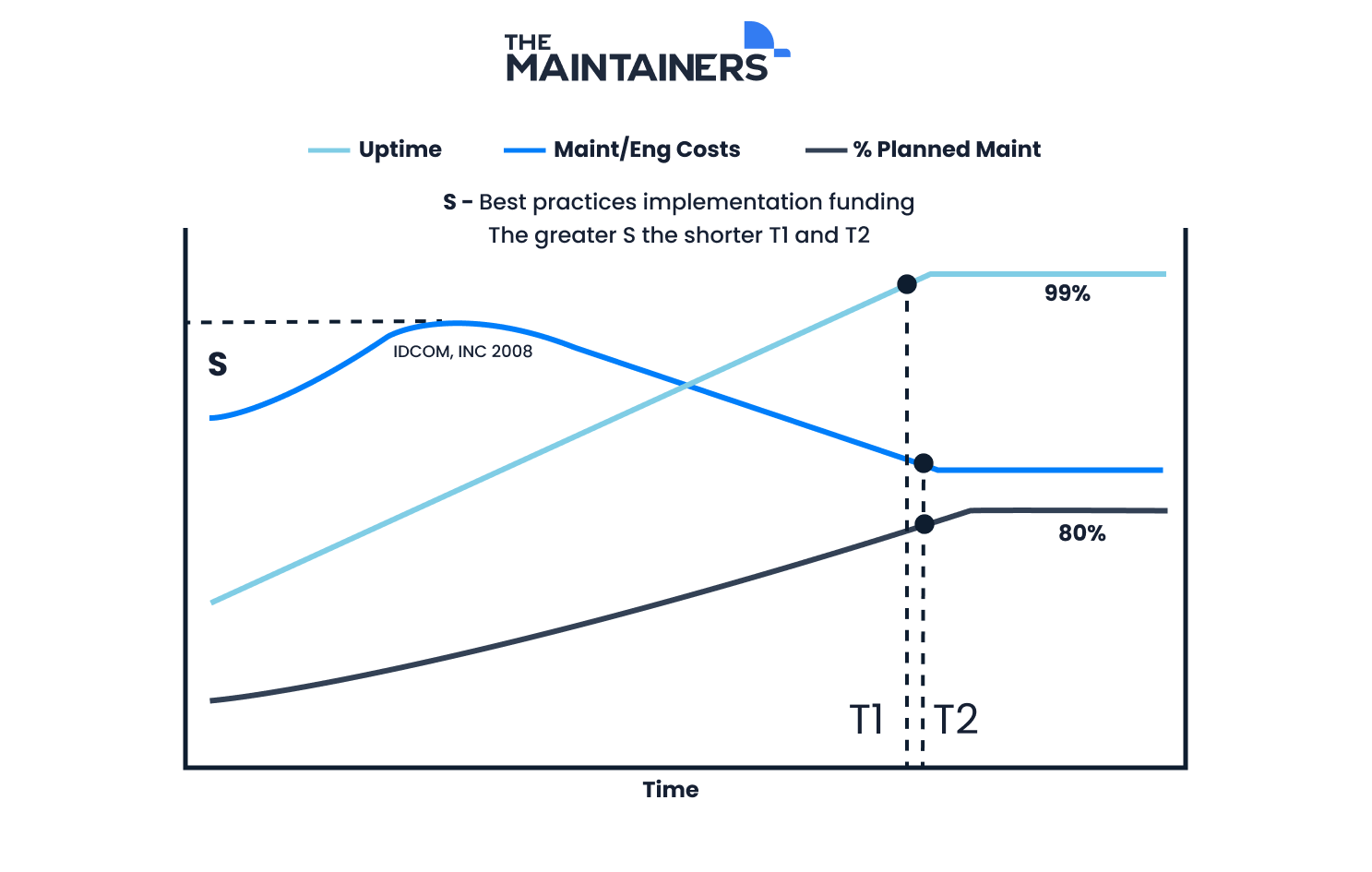
Source: Efficient Plant Mag
Ultimately, having an effective team, good tools, planning ahead, and investing in best practices will allow you to successfully implement good preventive maintenance strategies, increase your planned maintenance percentage, and reduce the instances of unplanned failure and downtime.
